History
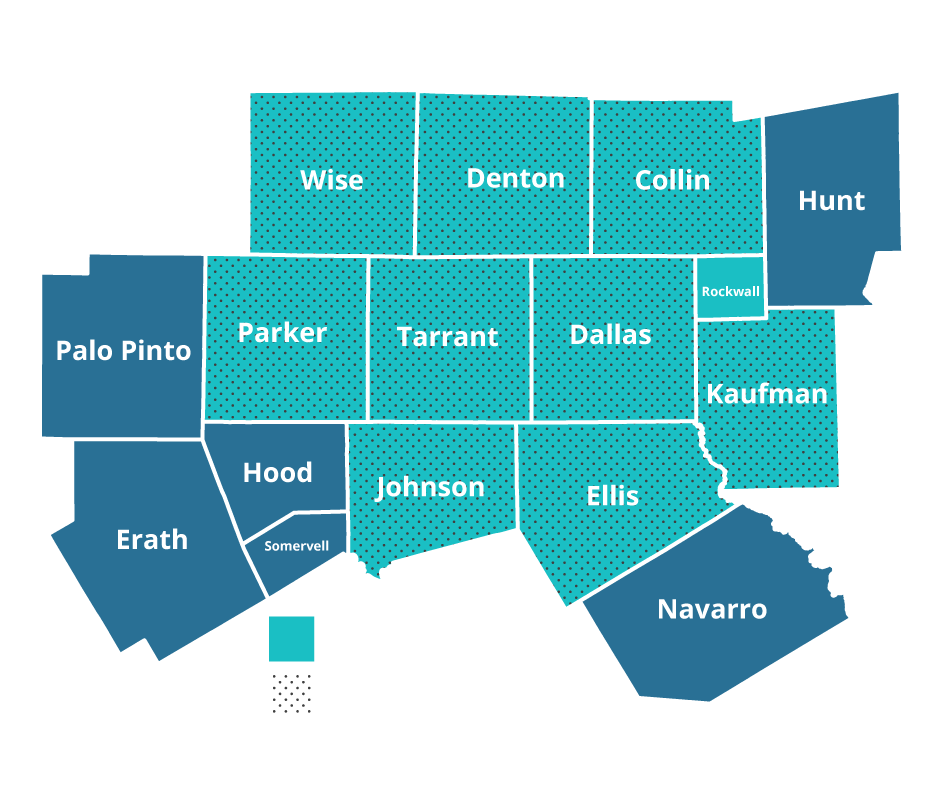
In 2018, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) designated nine counties in North Central Texas as "marginal" nonattainment for the 2015 8-hour ozone National Ambient Air Quality Standard (NAAQS). These standards are designed to protect human and environmental health, and ground-level ozone is monitored and targeted for reductions due to its potentially harmful effects.
The region has made significant progress since first being designated nonattainment in the 1990s. Information about the current ozone concentration and trends can be found here. The North Central Texas Council of Governments will continue to work with partners and encourage the involvement of residents and employees to meet the 2015 standard of 70 ppb or less to ensure a good quality of life for people of all ages.
Ozone Basics
Ozone forms when nitrogen oxides (NOx) and/or volatile organic compounds (VOCs) combine with sunlight and intense heat. Primary emissions sources include:
- Off-road vehicles such as construction equipment, lawn equipment, aircraft and locomotives
- Point area sources such as cement and power plants
- On road vehicles such as cars, trucks and buses
- Area sources such as oil and gas drilling, bakeries, paint shops and dry cleaners
- Biogenic sources like vegetation and forest fires
Historical emphasis has indicated that NOx reductions are the most appropriate way the region can lower ozone levels. On-road vehicle activities account for nearly half of the NOx inventory.
Ozone & Health
Inhaling ground-level ozone is especially dangerous for people who have asthma or respiratory problems, and they may experience increased frequency of asthma attacks and health care needs. Young children may also be at risk for developmental problems associated with ozone exposure. People without respiratory problems or asthma can also experience health effects from ozone exposure, such as the following.
- Coughing
- Throat irritation
- Chest tightening
- Pain, burning or discomfort when taking a deep breath
- Shortness of breath
Become familiar with the Air Quality Index (AQI) to better understand the severity of pollution and related health impacts. The AQI is used for reporting daily air quality levels. Colors indicate how polluted the air is and how to protect your health.